The Rise of Home Computers in the 1980s
The home computer market surged in the early 1980s, fueled by rapid technological advances and declining hardware costs, making home computers affordable to the average household across Europe and North America.

During the first half of the 80s, a wide range of 8-bit machines emerged, primarily based on two CPU architectures: the MOS 6502/6510 and the Zilog Z80.
Table: Popular 8-bit Computers and their CPUs
|
MOS-BASED |
ZILOG-BASED |
MOTOROLLA-BASED |
|
|
|
|
Commodore 8-bit (PET, VIC, 16, Plus/4, C64, and C128) |
Amstrad 464, 664, and 6128 CPC |
TRS‑80 Color Computer |
|
Apple 8-bit (Apple II and III) |
Sinclair's Z80, Z81, and ZX Spectrums |
Thomson Computers |
|
Atari 8-bit (400, 800, XL, and XE) |
MSX/MSX2 |
Sinclair QL |
|
Acorn 8-bit (Master, Atom, BBC, and Electron) |
TRS-80 Model |
|
|
Oric (Oric 1, Atmos, and Telestrat) |
Grundy NewBrain |
|
|
|
Jupiter Ace |
|
|
|
Enterprise |
|
|
SAM Coupe |
- Introduced in 1978, the Motorola 6809 is an 8-bit processor with some 16-bit features

Amstrad CPC (Colour Personal Computer)
The Amstrad CPC (Colour Personal Computer) line was a family of Z80-based home computers that competed with the ZX Spectrum and Commodore 64 in Europe. It gained strong popularity, especially in France and the UK.
- Processor: Zilog Z80, 4 MHz
- Operating Systems: AMDOS and CP/M
- Graphics: 27-color palette (up to 16 visible at once)
- Sound: AY-3-8912 chip with 3 channels (square wave and noise sounds)
CPC 464 (1984)
- Most affordable model
- 64K RAM and built-in cassette player
- Sold over 2 million units
CPC 664 (1985)
- Also had 64K RAM
- Came with a 3-inch floppy disk drive instead of a cassette
- Much rarer than the 464
CPC 6128 (1985)
- Released shortly after the 664
- 128K RAM, floppy drive, and CP/M+ system
- A big hit, selling over 1 million units
CPC+ Series (464+ and 6128+, 1990)
Released in 1990, the CPC+ was also based on the Z80 at 4 MHz, featuring considerably improved graphics and sound. The CPC+ sold well in France, but not as well in the rest of Europe. The US home computer market was off the radar of the CPC+.
- Updated versions of earlier models
- Still used the Z80 processor
- Better graphics: 4,096 colors (12-bit), 16 on screen at once
- Stereo sound and hardware sprites
- Sold well in France, less so elsewhere
 CPC Video Modes (27-color palette)
CPC Video Modes (27-color palette)
- 160×200 pixels with 16 colors (Mode 0)
- 320×200 pixels with 4 colors (Mode 1)
- 640×200 pixels with 2 colors (Mode 2)

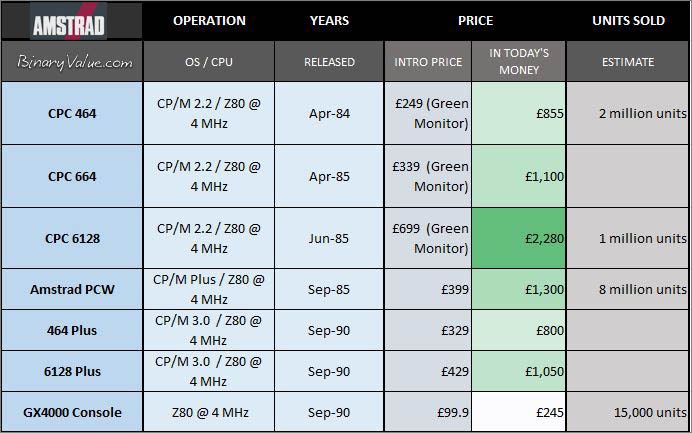
 Amstrad Sales
Amstrad Sales
Table: Amstrad 8-bit computers & units sold
![]()
Commodore 8-bit Computers
Founded by Jack Tramiel, Commodore International was a pioneer in home computing. Its most iconic machine, the C64, became the best-selling 8-bit computer of all time.
- Based on MOS CPUs
- The C64/C128 offered 16 colors, 8 hardware sprites (24×21 pixels), and smooth screen scrolling
- The sound chip was the impressive SID chip by MOS with 3 channels, 8 octaves, and 4 waveforms per audio channel (triangle, sawtooth, variable pulse, noise)
- The SID chip was included in the models C64, C128, CBM-II, and MAX
 C64 Basic Video Modes
C64 Basic Video Modes
- 320x200 pixels with 16 colors (HiRes mode)
- 320x200 pixels with 4 colors, by allowing mixing colors (MCI Mode)
- There are 5 additional video modes

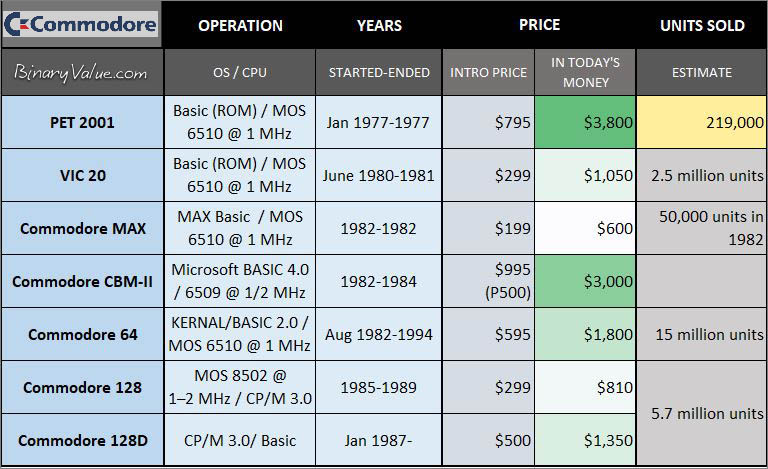
 Commodore Sales
Commodore Sales
Table: Commodore International 8-bit computers & units sold
» More about Commodore 64 | » More about Commodore 128

Sinclair 8-bit Computers
Launched in 1982 by Sinclair Research, the ZX Spectrum was one of the first truly affordable home computers. The legendary Clive Sinclair wanted to create a home computer for every family. To help with that, the first models were sold as "Starter Kits" at a very low price. The ZX-80 kit cost just £79.95 (or £99.95 if you wanted it already assembled), and around 50,000 were sold. But the first real hit was the ZX81, which sold 500,000 units in its first year alone.
- The ZX Spectrum family of computers sold about 5 million units worldwide before it was officially discontinued in 1992
- All ZX Spectrum models were based on the Zilog Z80 CPU
- Richard Altwasser made the hardware design
- Spectrum was sold as Timex in the US after Sinclair licensed the design to Timex Corporation
- There were many Spectrum clones in Russia and Eastern Europe, these clones were re-engineered to deal with the lack of components
- In 1986, Amstrad bought the entire line of Spectrum computers
128K -The advanced ZX Spectrum
The 128K was an improved Spectrum and the last computer made by Sinclair (before the Amstrad buyout).
- 128 KB of RAM, with disc commands
- 32 KB of ROM (including improved BASIC)
- 3-channel audio (AY-3-8912 chip)
- RGB monitor port
- RS-232 serial port and MIDI compatibility
+2/+3 Spectrum Computers (made by Amstrad)
In 1986, the entire line of Spectrum computers was manufactured by Amstrad. Amstrad released the +2 and +3 Spectrum models.
- The +2 is a 128K with a built-in cassette
- The +3 is a 128K with a built-in 3-inch disk drive (similar to the CPC 6128)
- The new Spectrums offered a spring-loaded keyboard and dual joystick ports
Sinclair QL (Quantum Leap)
Released in 1984, the QL was Sinclair’s attempt at a business computer, but it failed commercially. The QL is based on the Motorola 68008.
-
CPU: Motorola 68008, 7.5 MHz (32-bit internal, 8-bit external)
-
RAM: 128 KB (expandable to 640 KB)
-
Drives: Two built-in Microdrive tape loop cartridges
-
Ports: Two serial, joystick ports, expansion slots, and QLAN
-
Video:
-
256×256 with 8 colors
-
512×256 with 4 colors
-
-
Came with an office suite (word processor, spreadsheet, database, graphics)
 Spectrum Colors & Video Modes
Spectrum Colors & Video Modes
-
15 color shades (7 colors × 2 brightness levels, plus black)
-
Resolution: 256×192 pixels

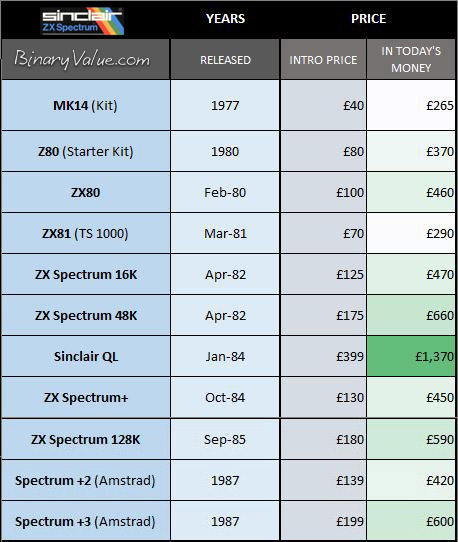
 Sales
Sales
Table: Sinclair 8-bit computers & units sold
■ 8-bit Computers
Binaryvalue.com (c) -Sources: CPCWiki.eu, Wikipedia, c64-wiki.com, studiostyle.sk






