Amstrad CPC — The European Home Computer Classic

Launched in 1984 and produced until 1990, the Amstrad CPC (Colour Personal Computer) was a series of Z80-based 8-bit home computers that played a key role in shaping the European computing scene. Competing with the likes of the ZX Spectrum and Commodore 64, the CPC line carved out a strong following, especially in France, the UK, and Germany.
- The CPC series, particularly the CPC 464 and CPC 6128, enjoyed significant commercial success, thanks to their all-in-one design, robust software support, and multimedia capabilities.
- In 1990, Amstrad introduced the CPC Plus range with enhanced graphics and stereo sound. However, by then, the 16-bit era had arrived, and the upgrade came too late to make a major impact.
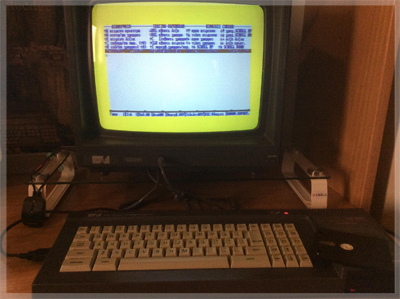
![]() CPC AT A GLANCE
CPC AT A GLANCE
- CPU: Zilog Z80 @ 4 MHz
- OS: AMSDOS / CP/M 2.2 / CP/M+
- Graphics: 27-color palette (CPC+ offers 4,096 colors)
- Sound: AY-3-8912 sound chip with 3 mono channels (CPC+ adds stereo output)
- Storage: Built-in cassette (CPC 464) or 3-inch floppy drive (CPC 6128)
- Software Library: Over 3,800 titles, mainly games but also productivity tools

 Graphics & Display Modes
Graphics & Display Modes
The original CPC models supported three primary video modes using a 27-color palette:
- Mode 0: 160×200 resolution with 16 colors
- Mode 1: 320×200 resolution with 4 colors
- Mode 2: 640×200 resolution with 2 colors
The CPC Plus series enhanced this with a 4,096-color palette (12-bit) and hardware sprites.
![]()
 Audio Capabilities
Audio Capabilities
The CPC series used the popular AY-3-8912 sound chip, also found in systems like the Spectrum, MSX, and Atari ST.
- Three mono channels producing square waves and white noise
- CPC+ series: Upgraded to 3 stereo voices, 8 octaves + 1 noise channel
 Operating System
Operating System
Amstrad CPCs came with ROM-based Locomotive BASIC, a fast and powerful BASIC dialect:
- Locomotive BASIC 1.0: Exclusive to CPC 464
- Locomotive BASIC 1.1: Standard on other CPC models
- Locomotive BASIC 2: Became a GEM-based GUI for Amstrad PCs
Supported operating systems included:
- AMSDOS (native disk OS)
- CP/M 2.2 & CP/M+ (for productivity software)
Later Operating Systems
FutureOS
- Developed in Z80 assembly since 1989
- Multitasking OS for CPC6128, CPC6128+, and others
- Still maintained as of 2022
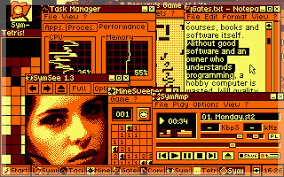 SymbOS
SymbOS
- Free multitasking OS with a Windows-like GUI
- Runs on Amstrad CPC, PCW, MSX2, and Enterprise 64/128
- Features pre-emptive multitasking and support for up to 2 TB drives
Software Library
The CPC series boasted a vibrant ecosystem:
- Over 3,800 titles, mostly games
- Hundreds of applications for word processing, graphics, and business use
- Games included classics and exclusives, many ported from arcade hits
 I/O Ports & Connectivity
I/O Ports & Connectivity
Rear Ports:
- Monitor out
- Printer port
- Expansion port
- Second floppy drive (not on CPC 464)
Left Side:
- 9-pin joystick port (Atari-compatible)
- Cassette port (except CPC 464)
- 3.5mm headphone jack
 Expansions & Upgrades
Expansions & Upgrades
The CPC was highly expandable. Key add-ons included:
- M4 Board: Adds Wi-Fi and SD card storage
- USIFAC II: USB hard disk interface
- Gotek Drive: Replaces 3" drive with USB support
- Dk’Tronics RAM upgrades: 64K–256K expansions
- Dandanator: Plug-and-play cartridge system with instant game loading
- CPLINK: Connects a Raspberry Pi as a co-processor
- Multiface II, MultiPlay MX4, and other peripheral adapters
 Related CPC Models
Related CPC Models

CPC 464 (1984)
- Entry-level model with 64K RAM and built-in cassette player
- Over 2 million units sold
CPC 664 (1985)
- Same 64K RAM but with a built-in 3" floppy drive
- Relatively rare today
CPC 6128 (1985)
- 128K RAM, CP/M+ support, and internal floppy drive
- Sold over 1 million units
Schneider CPC
-
Licensed versions of Amstrad CPCs for the German market (464, 664, 6128)
The CPC+ Series (1990)
Launched as the next-gen CPCs, the 464+ and 6128+ retained the Z80 CPU but added:
- 4,096-color palette, 16 colors on-screen
- Stereo sound with hardware sprites
- Cartridge slot and lightgun support
- Enhanced BASIC and CP/M 3.0
- Shared chipset with the GX4000 game console
While the Plus series found modest success in France, it struggled elsewhere and never entered the U.S. market.
 Amstrad Sales Figures
Amstrad Sales Figures
These are the Amstrad CPC sales highlights.
Table: Amstrad 8-bit computers & Units Sold
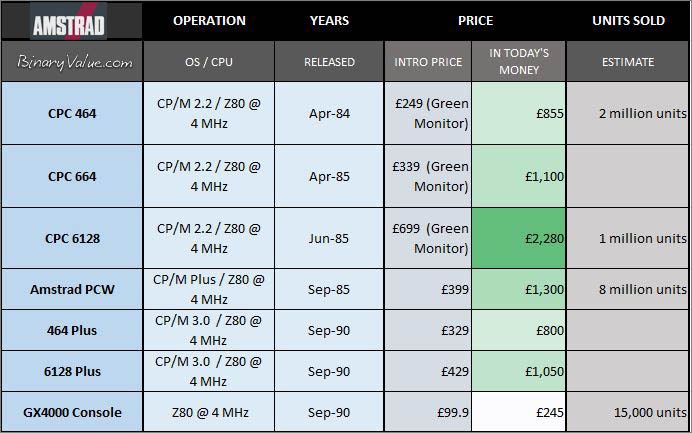
■ Amstrad CPC Computers
Binaryvalue.com 2022 (c) -Sources: CPCWiki.eu, Wikipedia











 TOP-10 APPS
TOP-10 APPS TOP-30 GAMES
TOP-30 GAMES

